Clientside WebApp
The Implicit grant type is a simplified flow that can be used by public clients, where the access token is returned immediately without an extra authorization code exchange step.
It is generally not recommended to use the implicit flow (and some servers prohibit this flow entirely). In the time since the spec was originally written, the industry best practice has changed to recommend that public clients should use either the authorization code flow without the client secret, or use the PKCE extension instead.
The Implicit Grant flow is initiated by redirecting the user in an embedded web browser inside of your application to the cidaas authz-srv/authz endpoint. cidaas will then display the cidaas-login page, allowing the user to enter their credentials or alternatively sign in with any other configured Identity Provider.
After the user has authenticated, cidaas will redirect the browser back to the redirecturi (also known as the Callback URL), passing along an access_token parameter in the hash fragment or the URL. The access_token is a JSON Web Token (JWT) and contains various attributes - referred to as Claims - regarding the user, such as the user's name, email address, profile picture etc.
The access_token can be decoded to extract the claims and you can use these inside of your application, to display a user's name and profile image for example.
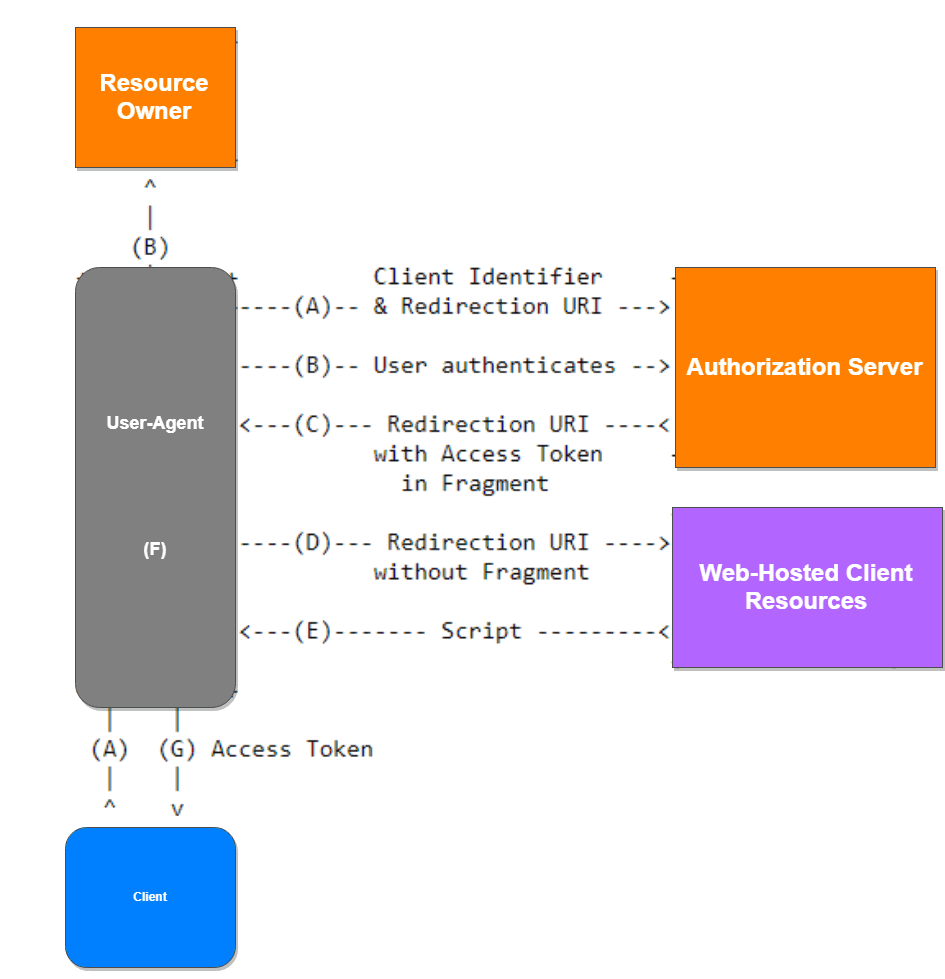
The Client initiates the flow and redirects the user to the Authorization Server.
The user authenticates
The Authorization Server redirects the user to the redirecturi with an "access_token" in the hash fragment.
The Client can now extract the token from the hash fragment.
How to implement the Implicit Grant
Register your App
The first thing you need to do is to create a new client in cidaas. A cidaas client maps to your application and allows it to use cidaas for authentication.
Navigate to the cidaas dashboard and click on the Apps menu option on the left. Create a new App by clicking on the Create App button.
The Create App page will open, allowing you to enter the name of your new application. Choose Client WebApp app type and click save button.
1. Get the User's Authorization
The URL used when authenticating a user is [https:///authz-srv/authz(). This is the initial endpoint to which a user must be redirected. This will handle checking whether any SSO session is active, authenticating the user and also potentially redirect the user directly to any Identity Provider to handle authentication.
To initiate the flow, send the user to the authorization URL:
https:///authz-srv/authz/? response_type=YOUR_RESPONSE_TYPE& client_id=YOUR_CLIND_ID& redirect_uri=https://YOUR_APP/callback& nonce=YOUR_CRYPTOGRAPHIC_NONCE state=YOUR_OPAQUE_VALUE
This endpoint supports the following query string parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| response_type | The response type specifies the Grant Type you want to use. This can be either code or token. For mobile applications using the Implicit Grant Flow this must be set to token |
| client_id | The Client ID of the Client you registered in cidaas. This can be found on the Apps page in the cidaas Dashboard |
| redirect_uri | The URL where the user will be redirected to after they have authenticated. For mobile applications you should specify this as [https://\[</span>](https://[]/authz-srv)/callback]\ (https://[</span>]%28https://[]/authz%29/callback]%28https://[</span>]%28 https:///authz-srv/callback]%28https://[</span>]%28 https:///authz-srv/callback]%28https://[</span>]%28 https:///authz-srv/callback%29)) Note: Be sure to add this URL to the list of Allowed Redirect URLs in the App Settings page inside the cidaas Dashboard |
| state | The state parameter will be sent back should be used for XSRF and contextual information (like a return url) |
2. Handle the Callback and obtain access token by implicit flow:
After the user has authenticated, cidaas will call back to the URL specified in the redirecturi query string parameter which was passed to the authz-srv/authz endpoint. When calling back to this URL, cidaas will pass along the access_token or id_token and the expire\_in**_ in the hash fragment of the URL, e.g.
https:///calback\\#access\\_token=eyJ0...&expires\\_in=3600
The access_token will be a JSON Web Token (JWT) containing information about the user. You can extract both of these values from the URL using basic string manipulation techniques in whatever programming language you are using.
As mentioned, the access_token is a JWT and you will need to decode this token in order to read the claims (i.e. attributes) of the user.
Once the JWT is decoded, you can extract the information about the user from the Payload of the access_token. This is a JSON structure and will contain the claims (attributes) about the user as well as some other metadata.
Request Object:
curl -X POST token-srv/token \ -H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \ -d 'grant_type=implicit &client_id=4d5e6e20-9333-42155-2890-5b7145533 &username=testuser%40gmail.com &password=test123 &scope=profile%20email%20phone%20identities%20offline_access &requestId=13f721ec-70cc-49b1-8134-dab0619e62b9'
Response Object:
{
"token_type": "Bearer",
"sub": "03769c03-1819-4e41-97b0-9d9ade94dd28",
"expires_in": 86400,
"id_token_expires_in": 86400,
"access_token": "eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsI......",
"state": "12345",
"sid": "f10744cf-2c5b-4848-9477-4a083d6483b8"
}
3. The access_token Payload
An example payload for an access_token may look something like this:
{
"sid": "0e002edc-4859-4a1e-b132-0982bef57964",
"sub": "cc28a557-ce0d-4896-9580-49639cbde8d5",
"isub": "400da8f2-a877-4c18-b864-2123efdda6f8",
"aud": "c17c6f2a-4729-4cf3-8963-76fb3fc0cc49",
"iat": 1528782823,
"auth_time": 1528782823,
"iss": "https://issuerdomain",
"jti": "a6d2629d-f2a4-4320-a40d-e632710062f7",
"scopes": [
"cidaas:admin_read",
"cidaas:admin_write",
"cidaas:admin_delete"
],
"roles": [
"USER"
],
"groups": [
{
"groupId": "CIDAAS_ADMINS",
"path": "/CIDAAS_ADMINS/",
"roles": [
"SECONDARY_ADMIN"
]
}
],
"exp": 1528869223
}
4. The payload above contains the following claims:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| sub | The unique identifier of the user. This is guaranteed to be unique per user and will be in the format (identity provider)(unique id in the provider), e.g. 2c68b74b-b8a3-4f2d-b8d5-b5c27d9db9c9. |
| role | Comma separated string value, contains roles of the user. |
| auth_time | Holds the value when the authorization happens. |
| iss | The issuer. A case-sensitive string or URI that uniquely identifies the party that issued the JWT. For a cidaas issued access_token, this will be the URL of your cidaas tenant. |
| exp | The expiration time. holds the milliseconds. |
| iat | The issued at time. holds the milliseconds. |
| exp_in | The expires in seconds. |
5. Verify the Token
Once your API receives a request with a Bearer access_token, the first thing to do is to validate the token. This consists of a series of steps, and if any of these fails then the request must be rejected. for more information